Budgeting and Saving are essential skills that unlock financial security and freedom for beginners. This guide covers budgeting basics and practical steps you can start today, including simple checks on income and expenses. By tracking income and expenses and setting clear, tangible goals, you can gain confidence, identify waste, and begin building an early financial cushion that grows over time. You’ll learn how to automate savings and rely on a simple tool that fits your life, helping you commit to regular contributions without feeling overwhelmed. Small, consistent actions now create momentum that protects you from surprises and supports your longer-term plans, such as a secure retirement or a flexible future.
In practical terms, money management shifts from rigid rules to a thoughtful spending plan that prioritizes needs, reduces waste, and supports future goals. Think of cash flow mapping, where you visualize every dollar as a tool to cover essentials, with room left for small pleasures and meaningful progress. A rainy-day fund, also called an emergency fund, acts as a safety net that prevents panic when life throws a curveball. Over time, you can automate transfers, use a monthly routine to review spending, and even try a monthly budget template to track progress. By focusing on sustainable habits rather than perfection, you build financial resilience and create room for the things that matter most.
Budgeting and Saving: Laying the Groundwork for Financial Security
Budgeting basics give you visibility and control over your money. By tracking income and all expenses, you illuminate your monthly cash flow and identify where you can cut back or reallocate funds. This practical awareness helps you answer the essential question: where is my money going, and how can I align spending with your priorities?
Pairing budgeting with deliberate saving strategies creates a reliable safety net. Automating savings ensures money is moved to a dedicated account on payday, reducing the temptation to spend it elsewhere. The pay-yourself-first approach reinforces discipline, while immediately building an emergency fund provides a financial cushion for life’s surprises and protects long-term goals from disruptions.
Mastering Budgeting Basics and Saving Strategies for Everyday Finances
To master budgeting basics in daily life, start with a simple, repeatable process: list all income sources, distinguish fixed expenses from variable ones, and set realistic spending limits. A monthly budget template helps you translate intention into action, allowing you to see how small adjustments in groceries, transportation, or entertainment can free up funds for savings.
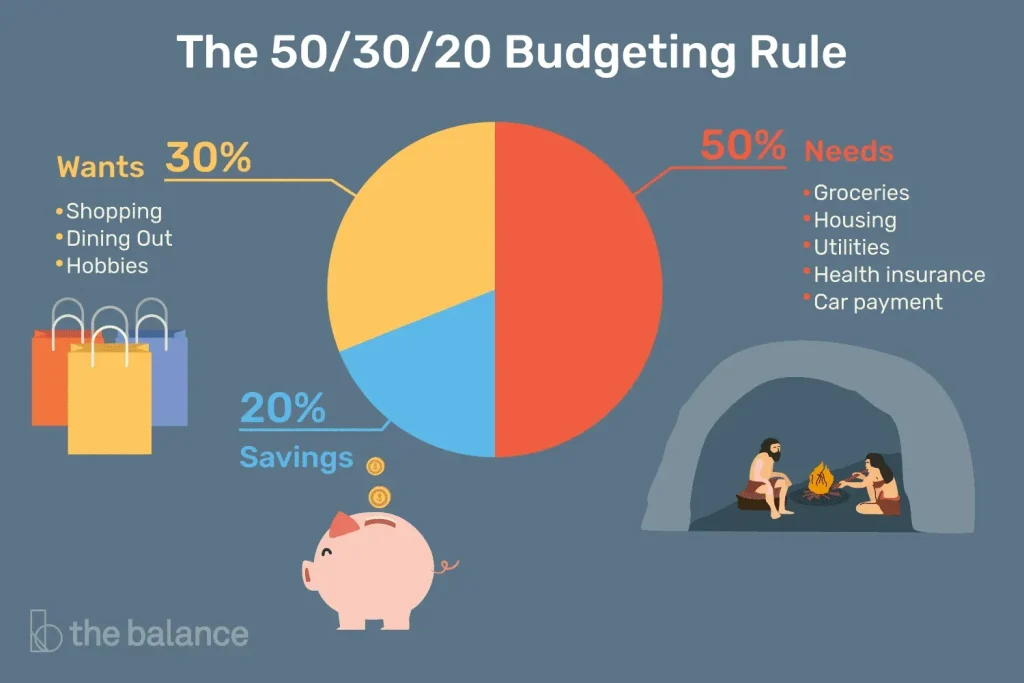
Focus on sustainable saving strategies that support both short-term wins and long-term security. Use the 50/30/20 framework as a flexible starting point, automate regular transfers to your savings, and gradually build an emergency fund that covers three to six months of living costs. Along the way, apply practical personal finance tips—track progress, review goals quarterly, and use budgeting tools to stay consistent and motivated.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are budgeting basics and how can I use a monthly budget template to implement saving strategies and build an emergency fund?
Budgeting basics start with tracking all income and expenses and organizing them in a monthly budget template. Use this template to implement saving strategies, for example by automating transfers to a savings account every payday and allocating a specific amount to an emergency fund. Start with a modest emergency fund target (for example $500-$1,000) and gradually grow toward 3-6 months of living expenses. A disciplined approach—combining budgeting basics, saving strategies, and a monthly budget template—gives you visibility and control over money, reduces stress, and shields you from unexpected costs.
How can personal finance tips and saving strategies work with budgeting basics and a monthly budget template to grow your emergency fund?
A solid personal finance plan begins with budgeting basics: know your income, track expenses, and set realistic goals. Pair saving strategies—such as paying yourself first and automating transfers—with a monthly budget template so saving becomes automatic. Focus on building an emergency fund that covers 3-6 months of living expenses to protect you from life’s surprises. Regularly review and adjust your budget as circumstances change, and use the template to maintain momentum toward your savings and debt-reduction goals.
| Section | Key Points | Practical Takeaways |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction |
|
|
| Budgeting Basics (Understanding Budgets) |
|
|
| Saving Strategies |
|
|
| Building a Practical Budget |
|
|
| Emergency Fund & Debt Management |
|
|
| Tools, Habits, & Practical Steps |
|
|
| Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them |
|
|
| 30-Day Action Plan |
|
|
| Conclusion |
|
|
Summary
Budgeting and Saving empower you to secure your financial future through deliberate, consistent practice. Start small, stay consistent, and let steady progress compound over time.