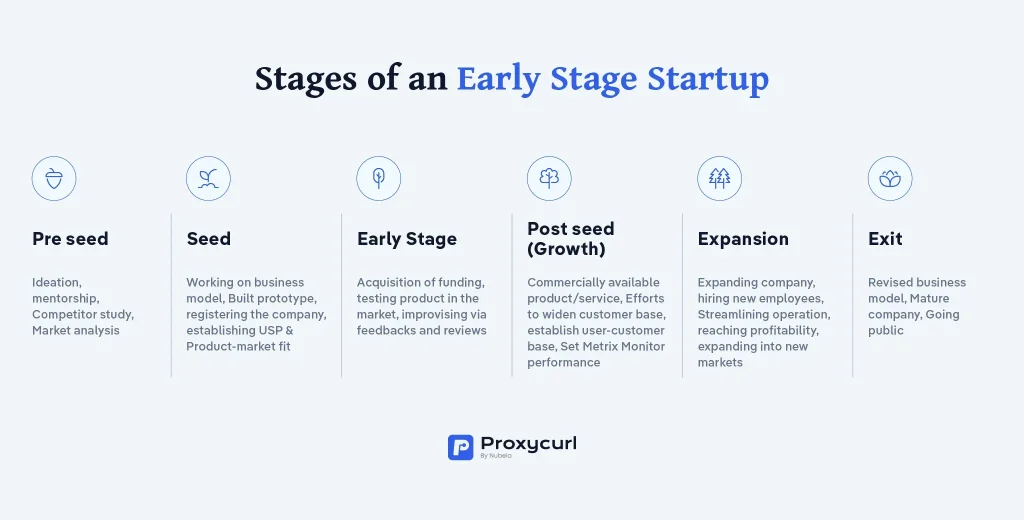
Entrepreneurship Essentials for Early-Stage Startups is a practical framework that guides founders from idea to traction, turning ambitious concepts into repeatable processes. In today’s fast-moving landscape, success rarely hinges on a single breakthrough product, but on a disciplined blend of clarity, speed, and learning. This concise guide distills the most impactful practices into actionable steps that founders can apply right away, from validating an idea to building a focused MVP strategy and engaging early customers. It also highlights early-stage startup tips, helping you allocate time, money, and energy where they matter most. Whether you’re refining your value proposition, testing market fit, or planning your next sprint, these essentials map a balanced path toward sustainable growth.
Viewed from a broader lens, these ideas become a blueprint for early-growth ventures seeking validation, speed, and disciplined execution. Founders are urged to pursue rapid experiments, ongoing customer discovery, and a lean product mindset that prioritizes learning over perfect speculation. A minimum viable product mindset – delivering core value quickly, gathering real user feedback, and adjusting pricing – keeps teams aligned with market needs without overbuilding. Financial prudence, clear metrics, and a collaborative culture round out the framework, supporting capital efficiency and sustainable momentum. Together these themes help startups navigate uncertainty while building something customers truly want.
Entrepreneurship Essentials for Early-Stage Startups: From Problem-Solution Fit to MVP Strategy
Entrepreneurship Essentials for Early-Stage Startups is a practical framework that moves founders from concept to traction. It starts with a clear problem worth solving and a credible solution that resonates with customers. By applying early-stage startup tips, founders interview potential users, quantify pain points, and validate that the proposed solution saves time, reduces cost, or lowers risk. The MVP strategy then becomes a learning engine—designed to test riskiest assumptions quickly and cheaply rather than to ship a perfect product.
With problem-solution fit and a disciplined MVP approach, you map a precise target market and segmentation (ICP). The more exact your segmentation, the easier it is to craft messaging, design features, and validate pricing. The MVP strategy supports rapid feedback loops and helps you decide whether to pivot, persevere, or halt development. This is where founder skills for startups come into play: listening to customers, running experiments, and aligning the team around a shared path.
Frequently Asked Questions
In the framework of Entrepreneurship Essentials for Early-Stage Startups, how can early-stage startup tips guide an MVP strategy and lean experimentation to validate problem-solution fit?
Start by clarifying the real problem and a differentiated value proposition, then design an MVP that tests the riskiest assumptions without overbuilding. Use lean experimentation: rapid A/B tests, hypotheses, and usage scenarios to gather customer feedback without heavy spend. Ensure the MVP aligns with your target market, pricing, and early traction goals to validate demand, usability, and the business model. This approach—rooted in early-stage startup tips—helps you learn fast, pivot if needed, and move toward product-market fit with disciplined capital use.
From the Entrepreneurship Essentials for Early-Stage Startups framework, how do founder skills for startups and bootstrapping a startup support a solid GTM plan and effective fundraising for startups?
Develop core founder skills for startups—leadership, clear communication, and disciplined hiring—to execute a focused GTM plan while keeping overhead lean. Practice bootstrapping a startup by prioritizing high-impact, low-cost experiments, tight cash-flow management, and meaningful metrics. Build a repeatable go-to-market process, gather early customer stories, and prove unit economics to de-risk fundraising for startups. With strong financial discipline and visible traction, you’ll craft compelling fundraising for startups narratives that resonate with investors.
| Essential | Topic | Focus / Actions |
|---|---|---|
| 1) Problem-Solution Fit and Value Proposition | Problem worth solving; credible solution; validate with potential users | Interview users, quantify pain, validate that solution reduces time/cost/risk; iterate messaging and differentiating value; informs pricing, positioning, and UX. |
| 2) Clear Target Market and Segmentation | Identify who has the problem and why they would choose you | Define an ICP; narrow focus; tailor messaging, features, and pricing; test MVP segments to learn where adoption is fastest. |
| 3) MVP Strategy and Lean Experimentation | Test riskiest assumptions with a lean MVP | Build small, measure everything, and learn faster than you spend; run rapid experiments to validate demand, usability, and pricing; decide to pivot, persevere, or halt. |
| 4) Customer Discovery, Feedback Loops, and Iteration | Continuous customer input to guide product decisions | Establish structured feedback loops (surveys, interviews, analytics); translate feedback into concrete product changes; prevent scope creep and misaligned priorities. |
| 5) Go-To-Market Strategy and Early Sales | Reach customers effectively with a scalable GTM plan | Pair GTM with MVP value proposition and pricing; define channels and milestones; build trust with early customers and collect case studies. |
| 6) Financial Discipline: Runway, Burn, and Cash Flow | Maintain financial health and resilience | Set realistic monthly spend; forecast revenue scenarios; plan contingencies; Bootstrap with cost awareness; prioritize initiatives with rapid payback. |
| 7) Key Metrics and Data-Driven Decision Making | Track a lean set of health metrics | Monitor activation, retention, churn, CAC, LTV, contribution margin, cash burn; use dashboards and weekly reviews to validate hypotheses and guide priorities. |
| 8) Team, Culture, and Founder Skills | Build the right team and culture | Develop leadership, communication, hiring discipline, and delegation; assemble a small, capable team; establish values and rituals; clarify decision rights. |
| 9) Legal, Compliance, and Intellectual Property Considerations | Understand the legal landscape and IP basics | Address incorporation, data privacy, contracts, IP protection; focus on high-impact issues while enabling product, customers, and growth. |
| 10) Fundraising Mindset and Strategy | Plan funding path and storytelling for investors | Map funding milestones; tailor pitches to seed/ VC preferences; build a compelling narrative around traction and unit economics; prepare for multiple investor types. |
Summary
This table summarizes the ten essential elements of Entrepreneurship Essentials for Early-Stage Startups, translating them into concise actions and focus areas that early founders can apply immediately. Each essential connects strategy to practical steps—from problem-solution validation and audience segmentation to MVP experimentation, customer feedback, GTM execution, financial discipline, data-driven decisions, team culture, legal considerations, and fundraising planning. Together, they form a practical framework for moving from idea to validated product, sustainable cash flow, and scalable growth.