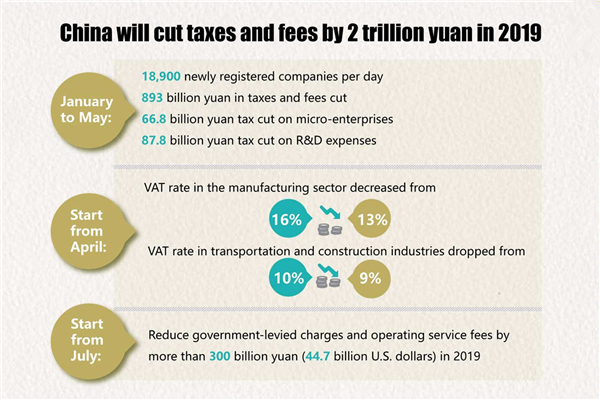
Policy shifts are a constant feature in modern economies, shaping strategies for growth and risk management across sectors. As governments adjust tax rules, regulatory standards, trade policies, and central banks tweak monetary settings, business leaders watch how policy shifts ripple through costs, demand, investment, and gauge the market reaction to policy shifts. Readers seeking clarity will note the policy shifts impact on economy as policymakers calibrate stimulus and restraint to sustain momentum. This article also examines how regulatory changes influence market sentiment and corporate planning. Finally, we connect the themes to practical guidance for leaders seeking resilient strategy amid evolving policy timelines.
Beyond the exact phrase policy shifts, analysts describe the evolving landscape through terms such as regulatory updates, government policy changes, and fiscal and monetary policy adjustments. Using Latent Semantic Indexing principles, the discussion groups related ideas around regulation, taxation, spending plans, central bank signaling, and business expectations to illuminate likely outcomes. This approach helps readers connect policy signals to practical effects on costs, incentives, investment, and competitive dynamics across sectors.
Policy Shifts and the Economy: Understanding Market Reactions
Policy shifts, whether driven by fiscal policy, central bank actions, or regulatory reform, redefine the operating environment for households, firms, and financial markets. The policy shifts impact on economy can hinge on the timing and credibility of signals, influencing when firms decide to invest, hire, or expand capacity.
Markets and business leaders closely watch the cadence of policy announcements, because the market reaction to policy shifts is often driven as much by clarity and credibility as by the policy details. In the realm of business news and policy impact, reporters translate complex changes into narratives that help executives reprice risk, adjust forecasts, and renegotiate contracts.
Sectoral channels show how policy moves ripple through the economy: tax incentives can spur R&D spending, while regulatory tightenings may raise compliance costs and extend cash conversion cycles. The macro feedback loops—growth, inflation, and currency moves—shape long-run competitiveness and investment, underscoring why policy shifts matter for strategy.
Economic Policy Changes and Business Performance: Navigating Regulation and Growth
Economic policy changes alter the cost of capital, incentives for investment, and the profitability math across sectors. When governments introduce tax reform, subsidies, or tariff adjustments, firms adjust pricing, budgeting, and capital deployment; these dynamics illustrate how policy changes shape business performance.
Strategic implications emerge as companies monitor regulatory calendars, adjust investor communications, and adapt to evolving market conditions. This connection—policy changes and business performance—highlights how firms translate policy signals into capital allocation, pricing, and growth initiatives.
By aligning scenario planning with anticipated policy pathways, leaders can cushion volatility and turn policy uncertainty into competitive advantage, building resilient supply chains, diversified sourcing, and flexible operations that adapt to both rules and timing.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do policy shifts impact the economy and business performance?
Policy shifts—such as fiscal changes, tax reforms, and central-bank actions—shape macro outcomes and, in turn, corporate results. The policy shifts impact on economy is driven by changes in GDP growth, inflation, and employment, which flow into costs, demand, and profitability for businesses. The timing, scale, and clarity of the policy signal matter: credible, transparent policy trajectories tend to reduce uncertainty and improve planning. Markets often move ahead of the actual implementation, illustrating the link between policy shifts and business outcomes, a common theme in business news and policy impact coverage.
What factors drive the market reaction to policy shifts and how should firms prepare for ongoing economic policy changes?
Key drivers of the market reaction to policy shifts include the credibility of the policy path and the clarity of timing—whether signals point to gradual tightening, reform, or delayed implementation. Other factors include current economic slack, the stance of monetary policy, global conditions, and the balance between short-term relief and long-term costs. Firms can prepare by scenario planning, maintaining flexible cost structures, diversifying suppliers, and providing transparent investor communications to reflect policy changes and their impact on business performance. Staying attuned to economic policy changes and the broader business news and policy impact helps executives adjust forecasts and capital plans.
| Aspect | What It Means / Key Points | Implications / Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Policy shifts are changes in government or central bank actions that alter the operating environment for households, firms, and financial markets. Examples include tax reform, interest rate changes, new regulatory guidelines, and long-term industrial policies. Their impact depends on timing, magnitude, signal clarity, and certainty around implementation. | They set the backdrop for all economic activity and market expectations. |
| Why They Matter / Macro Link | Policy shifts influence macro outcomes: fiscal policy affects aggregate demand (GDP, employment), and central bank decisions affect borrowing costs, spending, and investment. Together, they shape inflation, currency values, and long-run growth; effects appear in confidence and investment plans even before reforms are enacted. | Understanding these links helps anticipate demand, costs, and strategic risk. |
| Policy Shifts in the Economy | Direct influence on macro outcomes and business cycles; shifts in fiscal and monetary policy steer demand, inflation, and asset prices. | Macro dynamics hinge on how policy signals translate into real activity. |
| Policy Signals in Business News | Media translate policy announcements into narratives for executives, focusing on effects on supply chains, labor markets, and capital costs. | Clear reporting helps forecast models, contracts, and investor communication; credible policy messages can amplify market moves. |
| Mechanisms | The credibility of the policy path matters more than the policy itself. A clear strategy (gradual tapering, transparent reform timetable, or predictable regulation) reduces volatility; ambiguous or conflicting signals raise risk. | Market reactions depend on current slack, monetary stance, global conditions, and balance between short-term relief and long-term consequences. |
| Sectoral Impacts | Different industries react distinctly: finance/insurance respond to rates and regulation; tech/manufacturing to trade policies and incentives; energy/commodities to environmental policies and infrastructure. | Downstream effects propagate through supply chains, labor markets, and consumer spending; sector analysis helps interpret the broader picture. |
| Global & Regional Variations | Developed economies may rely on policy normalization and credible rulemaking; emerging markets experiment to spur growth and attract investment. | Investors monitor policy calendars, central bank communications, and reform agendas to anticipate regional differences. |
| Strategic Responses for Businesses | Practical steps: scenario planning, flexible cost structures, investor communications, talent strategy, and regulatory intelligence. | Proactive planning and information gathering help firms adapt to evolving policy environments. |
| Case Studies & Real-World Implications | Fiscal shifts like tax incentives for R&D affect profitability, capex, and supplier negotiations; monetary shifts like rate increases alter borrowing costs and expansion timelines. | Media emphasis on policy changes shapes business responses and capital allocation decisions. |
| Macro Trends | Sustained policy support for green energy, digital infrastructure, or upskilling can raise productivity and competitiveness; abrupt policy shifts can disrupt supply chains and investment sentiment. | Economic indicators—growth, inflation, unemployment, productivity—are viewed through the policy lens. |
| Interpreting Policy Signals | A disciplined approach distinguishes short-lived noise from durable shifts; analyses emphasize signal vs. noise and provide a framework for credible decision-making. | Leaders use this framework for capital allocation, pricing, and long-term planning. |
| Takeaways | Policy shifts influence both the economy and business news, shaping expectations and investment decisions; policy changes affect costs, demand, and profitability; market reactions are amplified by clear communication and credible trajectories; scenario-based planning and regulatory intelligence support resilience and long-term performance. | These elements help organizations navigate policy-driven volatility and seize opportunities. |
Summary
Table created to summarize key points about Policy Shifts.